Anxiety Disorder Symptoms, Hormonal Imbalance, and Histamine Intolerance: The Surprising Connection
Your brain is foggy. Making even small decisions feels overwhelming.
You’re worried about everything and it’s hard to sleep at night.
The fatigue that nearly overpowers you makes you want to go back to bed and pull the covers over your head and hide from everyone and everything.
You’re cranky, restless, and on edge. Panic attacks cause your heart to race and your palms to get sweaty.
Even if you only have only a couple of these problems, you may have generalized anxiety disorder. That’s the bad news.
The good news? You can feel at peace, happy, and calm again. The answer lies in balancing your hormones. But that’s not all. You’ll also need to get rid of problems like blood sugar imbalance that cause your hormones to get out of whack. Then there’s histamine intolerance, which is strongly linked to hormonal imbalances and anxiety.
Hormone Imbalance: The Victim Not the Villain
Imbalanced hormones are not the villains responsible for your anxiety disorder. They’re more like the victims of other problems happening in your body. That’s why as a functional medicine provider specializing in irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, and women’s fertility issues I see a lot of patients who also suffer from anxiety and panic attacks.
In fact, 75% of my patients present to my clinic with anxiety along with other issues like acid reflux, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), digestive issues, endometriosis and many more.
Hormones are actually responders, the language the body uses to talk to itself. Hormones express what they’re seeing in the different tissues around your body and tell your body how best to respond.
In other words, when hormones break, it’s not typically the root cause of your problems. Rather, the hormones shift in response to the root cause or causes of your health problems.
That said, working to adjust and balance hormones can help you feel better. When your hormones are balanced, you will have more energy and bandwidth to work on the real root cause underlying your health problems.
In this article, I’m going to dive into one common factor that breaks hormonal balance. Then I’ll hone in on one of the most important hormones for people suffering from anxiety disorder and its link to histamine intolerance.
I’ll also shed light on some of the other reasons for anxiety and panic attacks and let you know what you can do to feel less anxious and more at peace.
First, though, let’s talk about what generalized anxiety disorder actually is and its symptoms.
What Is Generalized Anxiety Disorder?
Everyone gets anxious from time to time. Work deadlines, tests at school, dealing with relationship problems or other stressors can all lead to occasional anxiety.
People with generalized anxiety disorder, on the other hand, experience ongoing worry or fear much of the time.
Often, people with anxiety disorder feel anxious or get panic attacks even while trying to make simple decisions. Generalized anxiety disorder can cause problems at work, in school, and in your relationships.
Symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder include :
- Difficulty concentrating or brain fog
- Fatigue
- Insomnia (difficulty falling or staying asleep)
- Irritability
- Restlessness
- Worry
Generalized anxiety disorder and panic disorder are some of the most common mental disorders in the United States. These are different types of anxiety disorders. Technically, conventional medicine considers panic attacks to be a separate disorder. However, in my experience as a functional medicine provider, most people aren’t going to have panic attacks without already having generalized anxiety disorder.
Symptoms of panic attacks include:
- Feeling out of control
- Feelings of impending doom
- Pounding heartbeat or rapid heart rate
- Shortness of breath, smothering, or choking
- Sweating
- Trembling
Past trauma can trigger panic attacks. But they can also happen in people who have never experienced any trauma.
Blood Sugar Imbalances Wreak Havoc on Hormones
One of the most common reasons why hormones break is because your blood sugar isn’t balanced. I have seen many patients get 90% better just by balancing their blood sugar.
Low blood sugar mimics anxiety. When your blood sugar crashes, the body attempts to push up blood glucose levels. It does this by making epinephrine, otherwise known as adrenaline, which triggers glucose production in the liver.
Increased adrenaline leads to a “fight-or-flight” stress response in the body. This same biochemical process is also linked to anxiety.
If you tumble into a chronic, on-going low blood sugar state, your body may boost its production of the stress hormone cortisol. This helps tissues in the body be less reactive to insulin, which boosts glucose circulation in the bloodstream. But high levels of cortisol can cause problems, too.
Guess what higher cortisol levels are also linked to? Anxiety.
What’s more, in my work with thousands of patients, blood sugar swings have been the biggest driver of fatigue, anxiety, and mood swings!
A functional medicine provider can order the right tests for blood glucose and insulin sensitivity. These include LDH (lactate dehydrogenase), HbA1c (hemoglobin A1c), SHBG (sex hormone binding globulin), fasting glucose, fasting insulin, and sometimes glucose response testing.
To resolve low blood sugar problems that show up on the tests, eat more healthy fats, which are easier to assimilate and digest.
High quality protein is also important. Back before I knew I had polycystic ovary syndrome – a condition linked to insulin resistance – I was eating vegan and vegetarian and chowing down on carbs. This was the wrong approach because anytime you have a problem with blood sugar or insulin, carbs are the bad guys.
The Soothing Effects of Progesterone
Your brain has receptors for sex hormones like progesterone. So it’s not surprising that progesterone can influence brain function and mood.
If you have anxiety, progesterone is one of your best friends.
Women with low progesterone levels are prone to anxiety. That’s why in conditions of low progesterone such as during PMS, post-childbirth, perimenopause, and menopause there’s an increase in anxiety and frequency of panic attacks.
Progesterone and its metabolite allopregnanolone act as a natural antidepressant, enhance mood, and relieve anxiety. Progesterone has a calming effect on the brain. It increases the actions of a feel-good, calming neurotransmitter known as GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid).
By giving GABA a helping hand, progesterone acts like a hormonal lullaby, helping you fall asleep easier and stay asleep longer.
What’s Histamine Intolerance Got to Do With It?
Histamine is a chemical released by some cells of the body. If you’ve ever had an allergic reaction or seasonal allergies, you’re likely familiar with its effects such as runny rose, sneezing, or hives.
Histamine isn’t always the bad guy. We need some histamine to release stomach acid and to help move food through the gut. The important thing is for histamine to complete its life cycle by being broken down and cleared from the body.
When that doesn’t happen histamine intolerance occurs. This is when the body makes too much histamine and too little of the diamine oxidase (DAO) enzyme needed to break it down.
Anxiety is a symptom of histamine intolerance. Other symptoms include headaches, fatigue, nausea, irregular menstrual cycles, sinus issues, digestive problems, tissue swelling, and dizziness.
In my experience, people most likely to suffer from histamine intolerance are people who are perfectionists. These are often the same people who suffer from anxiety and panic attacks. They want things to be a certain way and hold high expectations.
Characteristics of people most likely to develop histamine intolerance include:
- Academic overachievers
- Highly motivated
- Inner anxiety with a calm exterior
- Being competitive – with themselves and/or others
- Having obsessive/compulsive or ritualistic behaviors, or a need for structure and strong routine, feeling of order and control over things.
The above characteristics can actually be positive and work in your favor. If you have those characteristics you’re highly intelligent, super productive, and probably are successful in work and life. When your hormones are in balance these traits can work for you.
However, if your histamine is too high and your hormones are out of balance then you might develop poor stress tolerance, feelings of anxiety, and insomnia.
Progesterone Guards Against Histamine Intolerance
Progesterone enhances DAO, the enzyme that breaks down histamine. So progesterone helps histamine meet its maker and clear it from the body.
Estrogen dominance, on the other hand, boosts the body’s production of histamine. Women whose histamine production is estrogen driven will see flares of their problems either right before ovulation or more likely right before their period, because that’s when they’re naturally estrogen dominant.
Does anything else cause histamine intolerance besides estrogen dominance? You bet. Genetics can play a role. My own histamine intolerance was partly caused by genetics. But the gut plays a huge role, too. For me, my high histamine and hormonal imbalance came down to the “bad” organisms in my digestive tract (Helicobacter pylori, Giardia, and Candida albicans)
Leaky gut leads to lower levels of DAO and in turn high histamine. This is because the place where your body makes DAO is mostly mucosal barriers like the intestines.
If your liver isn’t working its best, that will cause problems, too. The liver detoxifies histamine. If its detox abilities are weakened, histamine will build up in the body. It’s just one more thing to fill your bucket up to the point of overflowing.
Other Hormones to Watch in Anxiety and Panic
In my patients with anxiety, I always keep an eye on other hormones besides progesterone. These include:
- Thyroid – If thyroid hormone levels are up and down like in Hashimoto’s it can mimic bipolar disorder. Low thyroid hormones are also linked to low progesterone.
- DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone) – DHEA is the most abundant circulating hormone. Balancing levels of DHEA can lead to better mood and less anxiety.
- Serotonin/Estrogen – Serotonin makes you feel content, happy, calm, and ready for sleep. It reduces anxiety and the tendency to think about sad or dark thoughts over and over (cyclical thinking or ruminating). You need estrogen to convert amino acids into serotonin.
- Cortisol – Cortisol is primarily produced by the adrenal glands. Adrenal fatigue can make you less likely to cope with stress. If you have a poor stress response, cortisol can be too high or too low. If cortisol goes up due to stress, your progesterone levels can take a tumble.
Strategies to Reduce Anxiety and Panic Attacks
Here are some simple changes you can make to feel calmer and less anxious:
- Reset your inner clock. First thing in the morning, immerse yourself in bright outdoor sunlight without wearing sunglasses. After sundown, expose yourself to dim light. If you’re not doing these things, neither dietary supplements nor hormone replacement therapy will work.
- Let go of toxic people, habits, and behaviors
- Seek professional therapy
- Practice stress management techniques like transcendental meditation, hypnotherapy, somatic therapy, nature immersion, the Gupta Program, and psychedelic journeying.
Natural Hormone Replacement and Dietary Supplements for Stress
Natural Progesterone - Please email office to discuss
A functional medicine provider can prescribe personalized, low-dose bioidentical progesterone. This can relieve symptoms of histamine intolerance and estrogen dominance.
Vitamin B6 supplements can help with histamine balance including PMS related to histamine. Vitamin B6 can:
- Help produce progesterone.
- Promote GABA synthesis.
- Convert L-tyrosine and 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) to dopamine and serotonin, respectively.
- Enhance DAO production and lower histamine.
Start with 50 mg of vitamin B6 in the form of P5P. You can take more under the guidance of a functional medicine provider.
Magnesium is a natural stress reliever. I prefer the chelated form of glycinate and the product Neuro-Mag.
L-theanine, a substance found naturally in green tea, produces calming brain waves. Passionflower (Passiflora incarnata) also has soothing effects.
Taurine is an amino acid that promotes formation and release of GABA, which quiets down excitatory signals in the brain. A typical dose is 250 mg – 1,000 mg/day.
Best for acute panic attacks rather than chronic anxiety, glycine is an amino acid that interferes with the release of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine. At the first sign of a panic attack, place two grams of glycine powder under the tongue and let it slowly dissolve. This process can be repeated every few minutes if necessary and, in most cases, the problem will resolve within 10 to 15 minutes.
Cannabidiol (CBD)
This phytocannabinoid has calming, soothing effects. In human studies, CBD reduced anxiety caused by a public speaking test in subjects with social anxiety disorder.
This lavender-derived substance (also known as Silexan™) promotes relaxation and calms nervousness.
I Can Help Balance Hormones and Relieve Anxiety
To find out whether the root cause of your anxiety disorder and panic attacks is blood sugar issues, low progesterone, or problems with other hormones, you’re going to need an experienced functional medicine practitioner. The first step is to book a free 15-minute troubleshooting call with me.
If after the call you come on board as a patient, I’ll order the best tests for you and develop a treatment plan based on your unique biochemistry. You will find out the steps you need to take to feel calmer and happier. I know anxiety isn’t easy but together we’ll find a solution to make your life easier.
The Truth About Hormones & Your Sex Drive
Which of these best describes your sex drive?
“Want it, need it, gotta have it!”
“Could take it or leave it...” or
“Don’t even think about it!”
Whatever you answer, there’s no shame.
Women are pretty reluctant to say our libido (or lack thereof) is one of our top health concerns. But when I dig deep with the women I work one-on-one with in my clinic, I find that almost all of them are struggling with their sex drive.
And personally, when I was struggling with hormone imbalance, my sex drive was non-existent. I thought it was just “normal.” After all, as women we are conditioned to believe we should want sex less than men.
Truth: healthy women have robust sex drives!
Our libido isn’t just dictated by whether our partner brings home flowers or we’ve shaved our legs - it is controlled by a complex group of hormones and neurotransmitters. Too much or too little of one or another can cause our sex drive to dwindle away or get out of hand.
That means that if your libido is lacking, you don’t just need to try lighting candles or new lingerie (although if your sex drive is healthy, that would sound fun instead of like a chore!). Balancing your hormones can restore a healthy libido.
Today, I want to explain how your hormones impact your sex drive. I hope this information empowers you - and if you have more questions or need more support, please reach out to me!
What This Article Can’t Do
Before I dig in to all the juicy hormone info, there are a couple other things I want to get out in the open.
First, most of the research on hormones has been done based on cisgender, heterosexual people and in heterosexual relationships. More research on hormones in other populations is long overdue. If you’re outside this group, some of this information will apply to you and some of it won’t - but I’d love to support you in overcoming hormone issues one-on-one until more inclusive research is available.
Secondly - as you're reading this I know symptoms of too much or too little of various hormones are going to jump out at you. But know this: the only way to diagnose hormone imbalances is with proper testing! That means blood, saliva, and/or urine testing.
Treatment for hormone imbalance is highly individualized, and I always recommend anyone who suspects hormone imbalance work one-on-one with a trained practitioner like myself for accurate testing and treatment! At the end of the article, I’ll share about my favorite hormone tests.
OK - disclaimers done - let’s get to the good stuff!
Estrogen - “The Feminine Hormone”
Estrogen is the hormone we associate with women. It makes women softer - both emotionally and physically. Estrogen is responsible for women’s curves: breasts, hips, and more fat on the butt! In studies of heterosexual men, women with higher estrogen levels were rated as more attractive.
It also increases a woman’s receptive sex drive—the part that makes her interested and open to penetration. Estrogen says “Take me now!” Women with higher estrogen levels may have more of a seductive sex drive - they are more likely to be receptive to sex, more likely to flirt and give “I’m available” signals, than they are likely to initiate it.
Testosterone - “The Masculine Hormone”
What hormone causes horniness? Testosterone is the hormone associated with men - but healthy women have testosterone, too. It helps us build muscle and causes us to feel more competitive and aggressive. In the bedroom, testosterone makes us want to initiate sex and governs the drive for genital sex and orgasms. Women with higher testosterone levels tend to have more of an aggressive sex drive and are more likely to initiate sex than wait for a partner to start things up. Interestingly, some post menopausal women have relatively higher testosterone levels (as compared to other hormones like estrogen) and may notice more of an interest in initiating at this phase in their lives.
Testosterone makes us less interested in relationships and commitment and more likely to want time alone (that’s what the Man Cave is for!). Women with higher testosterone levels tend to masturbate more, too. Too much testosterone can make us feel irritable - but too little can make us feel depressed.
Dopamine - “The Pleasure Chemical”
Dopamine isn’t exactly a hormone - it’s actually a neurotransmitter. Dopamine helps us anticipate pleasure - therefore having the drive and motivation to take action. It’s dopamine that makes us anticipate that sex = pleasure.
People who are low in dopamine tend to seem “flat” - they lack interest, enthusiasm, and get-up-and-go.
Testosterone increases the activity of dopamine in our brains, so supplementing with testosterone is often prescribed for women with low libido. But in my experience, this rarely works - or at least not without other support - probably because the issue isn’t just low testosterone, but also low dopamine. (Just another reason why you have to test!)
DHEA - “The Master Hormone”
DHEA is our most abundant circulating hormone. It’s produced both in the Adrenal glands and in the brain, and most of our other hormones are derived from it. DHEA levels peak in our 20s and start to decline from there - faster for some than others based on factors like your genetics and stress. Oral contraceptives are also know to lower DHEA levels.
Ideally, I like to see DHEA levels on the higher end of the normal range because DHEA can:
- Lower risk of depression
- Provide better function in old age
- Protect against immune suppression when cortisol levels are high (from stress)
- Prevent osteoporosis
- Maintain muscle mass
And of course, DHEA plays a major role in sex drive, orgasms, and sex appeal. Higher levels of DHEA in women correlated with higher rates of sexual desirability in studies. Most of our pheromones are derived from DHEA - scents that in the animal world dictate attraction and mating. Pheromones are often what make us feel an “instant connection” or drawn to someone. When a woman complains of low libido, I always test her DHEA levels first!
In times of stress, DHEA levels decrease significantly -and this can cause a cascade of low hormones throughout your body, since most other hormones are derived from DHEA.
Oxytocin - “The Love Molecule”
Oxytocin is a molecule that is triggered by physical touch. Oxytocin levels increase if you hug, hold hands, have sex, hold a baby - and even if you look at a dog! Levels of oxytocin also spike when you’re aroused and when you orgasm - it’s also what causes the uterus to contract during orgasm. If you’re in love, just thinking about the person can make your oxytocin levels go up.
Oxytocin helps you bond and feel love. It’s especially important for maternal bonding, and oxytocin levels rise during breastfeeding. Higher levels of oxytocin both reduce stress and rational thought - making it easier to “fall in love.”
Progesterone - “The Cock Blocker”
Does progesterone increase libido? In my practice I call progesterone the cock-blocking, (or clam-jamming) hormone. Basically, progesterone stops your sex drive. The effect of progesterone on your sex drive is so powerful, monks used to take the herb Vitex (aka Chaste Tree Berry!) to promote progesterone production and block their sex drive. Progesterone actually numbs the erogenous zones, meaning you’re likely to have dull orgasm with more stimulation - or no orgasm at all.
Many women have high levels of progesterone because they take hormonal contraceptives. The birth control pill contains a synthetic form of progesterone called progestin. Great birth control, right? Just kill your sex drive completely!
Progesterone isn’t all bad though - it promotes maternal behavior and has a mild sedative effect. It can make you feel calm, happy, and that everything is a-okay.
Does ovulation make you horny? In the second half of the menstrual cycle (after ovulation), progesterone is naturally higher. That makes sense biologically - once you’ve ovulated, your body won’t drive you to sex for reproductive reasons. When natural progesterone is balanced with estrogen, the dip in sex drive isn’t as strong and some women don’t notice it at all. Others might just be more interested in cuddling rather than going for an orgasm.
Prolactin - “The Nursing Hormone”
Prolactin is mostly associated with lactating women - it is the hormone that triggers your milk to let down after birth. Prolactin also tends to lower your sex drive - that’s why, in general, women have less sex when they are breastfeeding. Depending on your estrogen levels, you might retain some “receptive” sex drive even when prolactin is higher.
Promoting dopamine opposes prolactin. So if your prolactin levels are high and you’re NOT breastfeeding, using dopamine-promoting herbs can help lower prolactin and improve your sex drive. The only way to accurately gauge your prolactin levels is with testing!
Serotonin - “The Happy Chemical”
Serotonin is dopamine’s partner - together they are the two main neurotransmitters in the brain. Serotonin can impact your sex drive whether it’s too high or too low. Certain medications (like SSRIs) can cause high levels of serotonin. Dieting and chronically low calories can cause low serotonin, too.
Very high levels of serotonin dull your sex drive. That's why SSRI antidepressants have lowered sex drive and delayed/weaker orgasms as a side effect.
Conversely, low levels of serotonin can magnify your sex drive. In people with depression, low serotonin levels can even lead to sex addiction. In women with low serotonin, orgasms happen faster and easier. Men with low serotonin ejaculate right away.
Your Menstrual Cycle - “The Conductor”
Your menstrual cycle is like the conductor of all these hormones and chemicals. As the cycle progresses, hormone levels naturally rise and fall, leading to a shift in your sex drive.
At the beginning of your cycle, all hormone levels are low. Mid-cycle, estrogen and testosterone both spike - leading to an increase in sex drive (you’ll be both more aggressive and receptive to sex).
Many women also notice their libido peaks right before they start their period, as progesterone is naturally falling relative to testosterone. Your genitals will be more sensitive and it’s easier to orgasm during progesterone withdrawal.
During menses, some women have an increased sex drive - again because progesterone is lower relative to testosterone. But because serotonin levels can also drop during this time you might be grouchy too. Grumpy and horny!
The natural shift in hormones throughout the month can explain why sometimes you want sex more for the cuddling, emotional bonding, and skin-to-skin contact, - and why other times you just want an orgasm without all the bells and whistles.
Your Hormones & Your Libido
Our sex drive is completely dependent on our hormones. And as you’ve learned in this article, it’s not as simple as “more testosterone makes you horny!” Balanced hormones are the key to a healthy sex drive.
If your sex drive isn’t how you’d like it to be - either too much or too little - looking at your hormone balance is a great place to start. I know you’re sick of hearing me say this by now, but the ONLY way to accurately diagnose hormone imbalance is with advanced testing. You never want to “guess and check” by starting treatments or supplements for what you “think” is the problem. This can cause even greater imbalances that take more time and work to resolve.
Over the years I’ve used blood and saliva hormone tests - but now I almost exclusively use the DUTCH hormone test. This test is a kit your practitioner orders and you complete at home. It uses dried urine (that’s what the D and U stand for in DUTCH) to accurately test various hormone levels. It’s more accurate than saliva testing, and much simpler than blood testing. You just pee on a stick, let it dry, and mail it back to the lab.
Once I know a patient’s hormone levels, we can work together to come up with a plan to balance them. I never share exact protocols publicly because I’ve never had 2 patients who needed the exact same treatment! Hormones really are that unique.
If this article has resonated with you and you think hormone imbalances could be at the root of your sex drive struggles, I hope you’ll book a free 20-minute exploration call with my team. There’s zero obligation, but we’ll dive deep into your issues and then share what we can do to help.
Having come out the other side of hormone imbalance, I can tell you - having my sex drive back is great! (And my husband loves it too.) I want the health and radiance that comes from balanced hormones for all women. Book a 20-minute call for free here!
Why Your Gut Health and Microbiome Make-or-Break Your Hormone Balance
Acne worse than puberty, ten pounds that won’t budge, a period-induced mood swing that turns you into a totally different person-- these are sure signs your hormones are out of whack. The solution to hormone problems like these seems obvious: Fix your hormones.
But what if I told you that the first step to balanced, happy hormones (and clear skin, easy, regular periods, a healthy weight, and even-keeled moods) isn’t about estrogen, progesterone, or testosterone?
I’m going to let you in on a big secret about female hormones: They never break in isolation.
What does that mean? Simply that if something is not right with your hormones, it’s a sure sign that something ELSE is not working right in your body that is causing the hormone problems. If you’re having symptoms caused by imbalanced hormones, we have to do more than just treat the symptoms - and we even have to do more than just treat the hormone imbalance. (Prescribing artificial hormones is NOT the answer).
We have to go back even further and find out: What caused the hormone imbalance in the first place?
Finding and addressing the root cause of your hormone imbalance is the MOST important step to achieving hormone balance for life.
And 9 times out of 10, when we do the careful detective work to find the real root cause behind hormone imbalance, it’s actually related to gut health.
I know it sounds a little odd at first - but the health of our gut is actually closely tied to our hormone health. In this post, I’m going to explain the link between our gut and hormone health, and what you can do to optimize both.
The Gut-Hormone Dream Team
The gut and our hormones are meant to be in communication. They support each other and work together to make our body run smoothly. In fact, our intestinal cells have special receptors for hormones that allow them to detect hormonal shifts.
It’s intuitive that our hormone and gut interact, too - even women with symptom-free periods will report noticing slight changes in their bowel patterns before and during their menstrual cycle.
Both estrogen and progesterone impact gut motility & peristalsis - the rhythmic movement of the intestines that moves food from your stomach down through your intestines and eventually out of your body. Estrogen and progesterone play opposing roles in motility. Progesterone slows down motility in the gut by relaxing smooth muscle and slowing transit time (the time it takes for food to move out of your body). Even women without IBS or other digestive issues are more likely to feel mildly constipated, or just more “full” during the week prior to the period, when progesterone levels peak.
Estrogen, on the other hand, increases contractions of the smooth muscle in the intestines. When estrogen levels are just right, this helps keeps things moving. Estrogen also increases the diversity of your microbiome, which is a good thing for immune health. Estrogen levels drop off suddenly, twice, during a normal menstrual cycle: once right before ovulation, and again just prior to your period starting. This can cause spasm and fast motility in the digestive tract, which can cause diarrhea at these times (even in healthy women). For the same reason (sudden, dramatic drops in estrogen levels), this can also happen during perimenopause and menopause, too.
Pregnant women experience an increase in progesterone in early pregnancy and then again in the third trimester - this is responsible for the constipation so many women experience during pregnancy. The excess progesterone can also cause the sphincter in the upper GI tract to loosen, leading to heartburn and reflux.
When estrogen and progesterone are in balance, you’ll tend to have normal motility most of the time - neither constipation or diarrhea. (Unless you also have some gut infections like SIBO, Candida, or parasites….then you could still have constipation.)
The Estrobolome
Our gut and hormones do more than just “talk”-- your gut microbiome also regulates estrogen. The estrogen-regulating function of specific bacteria in the microbiome is called the “estrobolome.”
The estrobolome is really important to keeping healthy estrogen levels in the body -- but to understand why, you need to know how the estrogen cycle works. Here’s how it happens in a healthy system:
- Estrogen is produced in the ovaries (but also in the adrenal glands and adipose tissue to a lesser extent)
- Estrogens circulate in the blood, making their way to tissues in the breasts, brain, bones, uterus and elsewhere
- Eventually, the estrogens travel to the liver, where they are broken down and deactivated
- Detoxified estrogens are deposited in bile which is secreted into the intestines, and exits the body with the stool.
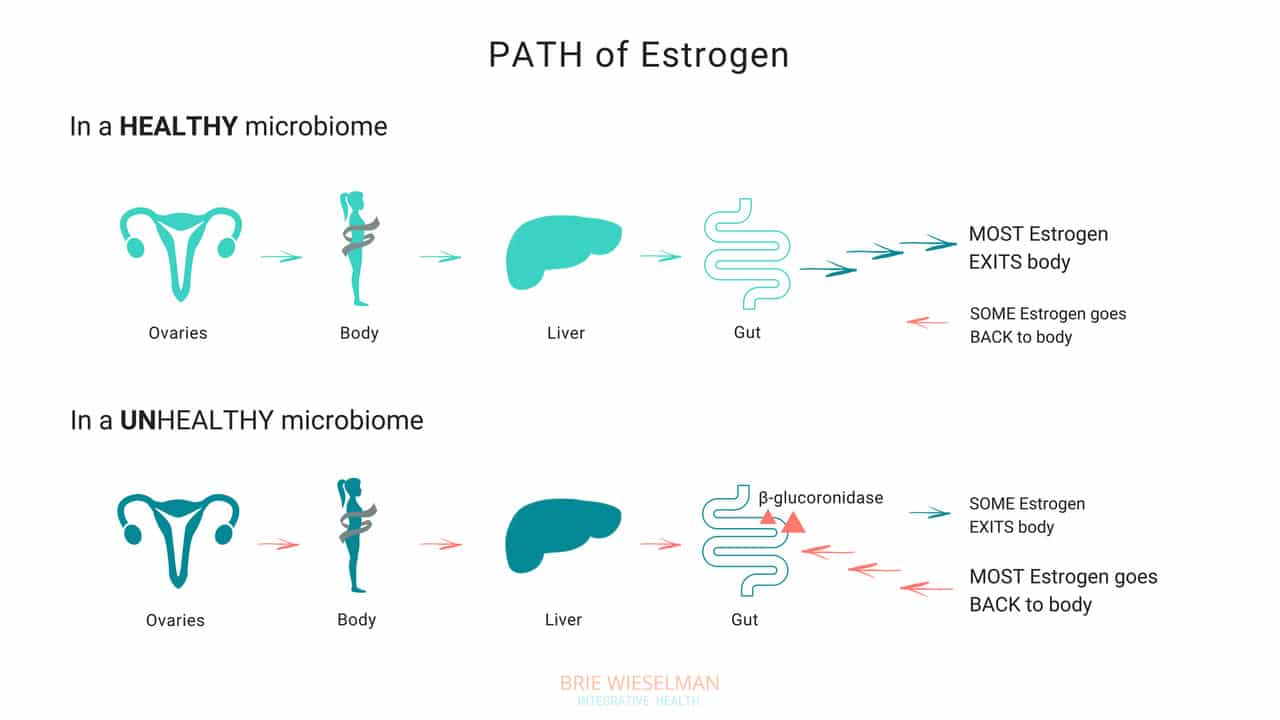
So, where does the gut come in? The gut - or more specifically, the estrobolome - regulates the amount of estrogens circulating in the bloodstream through the creation of β-glucuronidase, an enzyme which breaks down estrogen into to its “free”, or biologically active form.
But that isn’t all the gut does - it can also create its own estrogen, too!
Bacteria can manufacture estrogen-like compounds from foods that we eat. For example, lignans, found in plants like flax seeds, are converted into estrogen-like compounds when acted on by bacteria in the gut. On their own, they don’t have any hormonal properties, but once converted the can either promote uptake of our own more potent estrogens into receptor sites, or can compete for the same receptor sites,.
Newer research also suggests that the microbiome (and also specific types of probiotics) can produce its own estrogen and also signal glands around the body to produce it. We don’t yet fully understand exactly which strains of bacteria are responsible for all of these hormone modulating roles, but we do know that we want good overall proliferation, and greater species diversity.
When Things Go Wrong
The gut and your hormones are closely linked. You can see that both the gut and the hormone systems depend of each other to work properly - and when something goes wrong with either one, it spells trouble for the other.
Problems in the gut-hormone relationship usually start with the gut - but once the delicate balance is thrown off, it’s hard to know where to pin the blame. Imbalanced hormones cause gut problems, and gut problems cause imbalanced hormones.
Here are just some of the ways gut problems can lead to hormone imbalance:
Leaky Gut Syndrome: Leaky Gut Syndrome (aka Increased Intestinal Permeability) occurs when the tight junctions between cells in the intestine become “leaky” and allow toxins called LPS (which are fragments of dead bacterial cell walls) to pass from the intestine, into the bloodstream, and circulate through the body. It sounds crazy, but it’s actually common and causes a wide range of symptoms.
If you have leaky gut syndrome (with or without symptoms), you are more vulnerable to developing hormonal imbalances. Why? Because leaky gut causes widespread inflammation throughout the body. LPS is known to cause inflammation in any tissue that it comes into contact with, and in the ovaries, the result is suppressed progesterone production. (Women with higher levels of LPS in the blood had elevated markers of inflammation in fluid inside the ovary (follicular IL-6), and correspondingly low progesterone production.)
Studies show that infections, allergic reactions, being born by cesarean section, and even chronic stress can all cause inflammation in the gut, as well. And inflammatory conditions like obesity and inflammatory bowel disease are associated with disrupted menstrual cycles and infertility.
If you’re not having digestive symptoms like bloating, diarrhea, or constipation, you may think you don’t have leaky gut syndrome - but leaky gut may not show up as digestive symptoms, depending on the person. Even without digestive symptoms, the “silent” inflammation caused by leaky gut affects nearly every other aspect of health - especially our hormones.
Gut Dysbiosis: Your intestines are filled with trillions of bacteria, fungi, and even some viruses, that are all collaborating to keep your system running smooth and healthy. These bacterial cells and their genes are called your microbiome, and they live not just inside the intestines, but on every surface of your body, from your skin, to your eyes, your lungs, vaginal walls, and bladder. When the microbiome gets disturbed and the type or number of bacteria is damaged, we call it gut dysbiosis.
Along with your brain, your microbiome regulates the expression of your hormones, and can restrict or promote hormone production elsewhere in the body. The bacteria in your microbiome are like air-traffic control for hormones. In addition to signalling other glands in the body to dial up or down the volume on hormone production, your gut flora regulate hormone metabolism post-production, by either helping (or hindering) detoxification of already-used hormones, when they are being cleared from your system to make way for new fresh hormones.
To work properly, your microbiome needs the right bacteria, in the right amount. When the type or number of bacteria gets messed up (from something like poor diet & stress, an infection or parasite, or even just a course of antibiotics) your gut can no longer perform it’s hormone-regulating functions properly.
Increasing reactions to food, bloating, skin outbreaks, constipation, stubborn weight that won’t budge despite your best efforts, and even heavy periods— can all be signs that your microbiome is compromised and you’re unable to properly metabolize hormones like estrogen in the gut. Ultimately, this causes a build up of hormones in your system, which shows up as worsening of your PMS, period symptoms, or menopausal symptoms, and leaves you bloated and moody.
Estrobolome Dysfunction: Remember, the estrobolome are the specific bacteria in the microbiome responsible for regulating estrogen in the body through the production of the enzyme β-glucuronidase. Disruption of the estrobolome are really a type of dysbiosis. The estrobolome can be damaged in the same way the rest of the microbiome gets hurt: common triggers are stress, poor diet, and especially antibiotic use.
If the estrobolome bacteria become overgrown, the result is too much beta-glucuronidase being made. This causes already-detoxified estrogen to be reabsorbed and recirculated, in really high levels. This leads to a state of estrogen dominance. And estrogen dominance creates all kinds of chaos - PMS, cramps, fibroids and cysts, endometriosis, PCOS, heavy bleeding, infertility, a zapped sex drive, and weight gain. And of course, it can increase the risk of certain types of breast and uterine cancers.
And while it’s clear that we don’t want gut bacteria producing too much beta-glucuronidase enzyme, we actually don’t want them under-producing it either! When women have extremely low microbial diversity or even just extremely low levels of bacteria in the gut (think: excessive antibiotic use), the decrease in beta-glucuronidase causes a reduction in circulating free estrogens. Excess estrogen isn’t a good thing, but insufficient estrogen levels, especially in post-menopausal women, isn’t good for our health either! Estrogen is critical for maintaining healthy brain cognition, bone density, gut health, and cardiovascular health.
It isn’t just these gut problems that could be causing your hormone issues. The gut-hormone connection is a two-way street: here are some of the ways imbalanced hormones can wreak havoc on your gut health:
- Gallstones - women get gallstones twice as often as men! Estradiol (one of the types of estrogen) increases cholesterol levels in bile produced in the liver. (Cholesterol is the building block of our reproductive hormones, so when they are detoxified and broken down, cholesterol is released.) This increased saturation slows bile flow, which can lead to more stone formation.
- Leaky Gut - While inflammation caused by leaky gut can lead to hormone imbalances, low estrogen levels can also contribute to leaky gut. The epithelial layer of the intestinal wall needs estrogen to and keep it healthy and elastic. Leaky gut has been associated development of food sensitivities, autoimmune diseases, weight gain, acne, depression and anxiety, as well as almost every chronic illness you can think of.
- IBS - researchers know that estrogen and progesterone levels have an impact on the development of IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome). Symptoms of IBS include diarrhea, constipation, bloating, pain, and food intolerances.
Here’s the bottom line: if you want healthy hormones, you have to fix your gut!
Healthy Gut, Healthy Hormones
We know that we need a healthy gut to get healthy hormones - but what messed up your gut in the first place?
It’s a fair question, and not always easy to unravel. These are the most common causes for gut problems I see in my clinic - but there are many more (and most people have more than one contributing!)
Antibiotics: A single dose of the antibiotic Augmentin can kill off up to 90% of your gut flora - and most people are prescribed a 5-day course! Gut flora will regrow, (although it can take up to a year) but what types take hold and flourish impacts every aspect of our health. Generally we lose lactic-acid-producing species (like L. Acidophilus) first. This causes pH to go up in the intestines. Good colonic bacteria flourish in a more acidic environment, so in a less acidic environment, unfavorable strains can grow.
Toxins: Pesticides, herbicides, glyphosate from GMO corn and other foods, environmental chemicals, infections, and even stress can negatively shift the microbiome.
Diet: Eating a diet low in fermentable fibers and resistant starches (found in veggies, fruits, nuts, seeds, legumes, and grains) will also decrease bacterial diversity. Dairy, sugar, and gluten are major culprits in promoting bacterial imbalances.
The Pill: Contraceptive pills damage your microbiome as much as antibiotics do! The pill is known to promote candida overgrowth and SIBO (small intestine bacterial overgrowth) as well. Recent research has linked oral contraceptive use to development of inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis, too.
The good news is there is a lot we can do to support better gut health - leading to better hormone health.
The best ways to support a healthy microbiome for healthy hormones, is through a diverse whole food diet, optimizing digestion, and taking steps to lower inflammation.
- Eat fermented foods - Sauerkraut, yogurt, kefir, kombucha, etc.
- Eat prebiotics/fiber - Found in root vegetables, flax seed, psyllium, beans, seeds, nuts, fruits and veggies. Women who eat more fibers from plants clear greater levels of estrogen in their stool.
- Take probiotics - In particular, Lactobacillus Acidophilus helps lower beta-glucuronidase!
- Optimize the environment of your digestive tract so good bacteria flourish there - This is similar to prepping the soil in your garden beds. Digestive secretions like pancreatic enzymes, stomach acid, and bile help optimize the conditions in the gut to promote the desirable bacteria. Taking these supplementally if you are deficient can help prime the gut for healthy colonization.
Get Your Gut & Hormones Humming
Every woman’s health is unique - but if a woman is having hormone symptoms, it almost always comes back to gut health! Heavy periods, adult acne, and PMS may not seem like they are related to your gut, but they so often are! That’s why I always test and treat the gut alongside hormone balance problems in my clinic.
Remember, our hormones don’t break in isolation! It’s almost always a sign of a problem somewhere else in the body. If you are struggling with your hormones, don’t forget to consider your gut health!
I hope this article and my suggestions for optimizing gut health help you. Need more help unraveling the root cause of your hormone issues? Want to run the right testing, so that you can really know for certain, what’s going on with your hormones and gut? I love to help women like you get back to radiant health so they can live big! If you’re interested in learning more about how I do this, you can book a free 20-minute prospective patient call here.